- Affordable Edge.
- 831.206.2385
- info@centralcoastpatent.com
Blockchain patent application from consulting giant Accenture aims to revolutionize its logistics network.
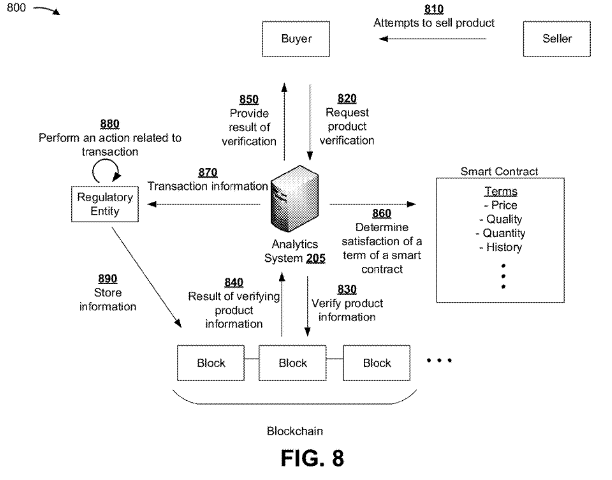
At the core of this technology are methods of using testing devices and smart contracts to document each stage of a shipment from seller to buyer and to test the chemical status of the product at each leg of it’s journey by truck, rail, air and vessel.
The testing devices can be stationary and robotic and are able to monitor temperature, humidity, barometric pressure and use analyzing techniques such as nuclear magnetic resonance, gas chromatography mass spectrometry, fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, high performance liquid chromatography, DNA extraction, X-ray fluorescence, energy dispersive, laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, ion chromatography, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and more.
The smart contracts will have predefined parameters and tolerances that will be authenticated by the devices and those events will be recorded in the blockchain for each step of the transaction.
The blockchain will provide an immutable and transparent history of the shipment for the buyer, seller and authorities to review.
There will be no need for any slow moving and fallible third parties to verify and process shipping documentation and events that transpired from end to end.
As with smart contracts, the buyer and seller do not need to know or trust each other.
Source: USPTO
CCPA – Blockchain Patent Law Experts